B. Illustration 2
Consider a netting set with three credit derivatives: one long single-name CDS written on Firm A (rated AA), one short single-name CDS written on Firm B (rated BBB), and one long CDS index (investment grade). All notional amounts and market values are denominated in USD. This netting set is not subject to a margin agreement and there is no exchange of collateral (independent amount/initial margin) at inception. The table below summarizes the relevant contractual terms of the three derivatives.
Trade # Nature Reference entity / index name Rating reference entity Residual maturity Base currency Notional (thousands) Position Market value (thousands) 1 Single-name CDS Firm A AA 3 years USD 10,000 Protection buyer 20 2 Single-name CDS Firm B BBB 6 years EUR 10,000 Protection seller -40 3 CDS index CD X.IG Investment grade 5 years USD 10,000 Protection buyer 0 According to the Standards, the EAD for un-margined netting sets is given by:
EAD = 1.4 * (RC + PFE)
1. Replacement Cost Calculation
The replacement cost is calculated at the netting set level as a simple algebraic sum (floored at zero) of the derivatives’ market values at the reference date. Thus, using the market values indicated in the table (expressed in thousands):
RC = max {V - C; 0} = max {20 - 40 + 0; 0} = 0
Since V-C is negative (i.e. -20,000), the multiplier will be activated (i.e. it will be less than 1). Before calculating its value, the aggregate add-on needs to be determined.
2. Potential Future Exposure Calculation
The following table illustrates the steps typically followed for the add-on calculation:
Steps Activities 1. Calculate Effective Notional Calculate supervisory duration
Calculate trade-level adjusted notional = trade notional (in domestic currency) × supervisory duration
Calculate trade-level effective notional amount = trade-level adjusted notional × supervisory delta × maturity factor
Calculate effective notional amount for each entity by summing the trade-level effective notional amounts for all trades referencing the same entity (either a single entity or an index) with full offsetting2. Apply Supervisory Factors Add-on for each entity in a hedging set = Entity-level Effective Notional Amount × Supervisory Factor, which depends on entity’s credit rating (or investment/speculative for index entities) 3. Apply Supervisory Correlations Entity-level add-ons are divided into systematic and idiosyncratic components weighted by the correlation factor 4. Aggregate Aggregation of entity-level add-ons with full offsetting in the systematic component and no offsetting in the idiosyncratic component Effective Notional Amount
The adjusted notional of each trade is calculated by multiplying the notional amount with the calculated supervisory duration SD specified in the Standards.
d= Trade Notional × SD = Trade Notional × {exp(-0.05×S) – exp(-0.05 × E)} / 0.05
Trade Notional Amount S E Supervisory Duration SD Adjusted Notional d Trade 1 10,000,000 0 3 2.785840471 27,858,405 Trade 2 10,000,000 0 6 5.183635586 51,836,356 Trade 3 10,000,000 0 5 4.423984339 44,239,843 The appropriate supervisory delta must be assigned to each trade: in particular, since Trade 1 and Trade 3 are long in the primary risk factor (CDS spread), their delta is 1; in contrast, the supervisory delta for Trade 2 is -1.
Trade Delta Instrument Type Trade 1 1 linear, long (forward and swap) Trade 2 -1 linear, short (forward and swap) Trade 3 1 linear, long (forward and swap) Thus, the entity-level effective notional is equal to the adjusted notional times the supervisory delta times the maturity factor (where the maturity factor is 1 for all three derivatives).
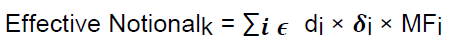
Trade Adjusted Notional Supervisory Delta Maturity Factor Entity Level Effective Notional Trade 1 27,858,405 1 1 27,858,405 Trade 2 51,836,356 -1 1 -51,836,356 Trade 3 44,239,843 1 1 44,239,843 Supervisory Factor
The add-on must now be calculated for each entity. Note that all derivatives refer to different entities (single names/indices). A supervisory factor is assigned to each single-name entity based on the rating of the reference entity, as specified in Table 1 in the relevant Standards. This means assigning a supervisory factor of 0.38% for AA-rated firms (Trade 1) and 0.54% for BBB-rated firms (for Trade 2). For CDS indices (Trade 3), the supervisory factor is assigned according to whether the index is investment or speculative grade; in this example, its value is 0.38% since the index is investment grade.
Asset Class Subclass ρ SF Credit, Single Name AA 50% 0.38% Credit, Single Name BBB 50% 0.54% Credit, Index IG 80% 0.38% Thus, the entity level add-ons are as follows:
Add-on(Entity) = SF × Effective Notional
Trade Effective Notional Supervisory factor SF Add-on (Entity) Trade 1 27,858,405 0.38% 105,862 Trade 2 -51,836,356 0.54% -279,916 Trade 3 44,239,843 0.38% 168,111 Supervisory Correlation Parameters
The add-on calculation separates the entity level add-ons into systematic and idiosyncratic components, which are combined through weighting by the correlation factor. The correlation parameter ρ is equal to 0.5 for the single-name entities (Trade 1-Firm A and Trade 2-Firm B) and 0.8 for the index (Trade 3-CDX.IG) in accordance with the requirements of the Standards.
Add-on(Credit) = [ [ ∑k ρk CR × Add-on (Entityk) ]2 + ∑k (1- (ρk CR)2) × (Add-on (Entityk))2]1/2
Trade ρ Add-on(Entityk) ρ × Add-on(Entityk) (1 – ρ2) (1 – ρ2) × (Add-on(Entityk))2 Trade 1 50% 105,862 52,931 0.75 8,405,062,425 Trade 2 50% -279,916 -139,958 0.75 58,764,860,350 Trade 3 80 % 168,111 134,489 0.36 10,174,120,000 Systematic Component 47,462 Idiosyncratic Component 77,344,042,776 Full offsetting No offsetting Add-on Aggregation
For this netting set, the interest rate add-on is also the aggregate add-on because there are no trades assigned to other asset classes. Thus, the aggregate add-on = 346,878
Aggregation of entity-level add-ons with full offsetting in the systematic component and no offsetting benefit in the idiosyncratic component.
Systematic Component 47,462 Idiosyncratic Component 77,344,042,776 Thus,
Add-on = [ (47,462)2 + 77,344,042,776 ]1/2 = 282,129
Multiplier
The multiplier is given by
multiplier = min {1; Floor+(1-Floor) × exp [(V-C)/(2×(1-Floor)×Add-onagg)]}
= min {1; 0.05 + 0.95 × exp [-20,000 / (2 × 0.95 × 282,129)]}
=0.96521
Final Calculation of PFE
PFE = multiplier × Add-onagg = 0.96521 × 282,129= 272,313
3. EAD Calculation
The exposure that would be risk-weighted for the purpose of counterparty credit risk capital requirements is therefore:
EAD = 1.4 * (RC + PFE) = 1.4 x (0 + 272,313) = 381,238