4.3.2. Identification of Beneficial Owners and of Ownership and Control Structure
4.3.2.1. UAE Requirements
As discussed in section 4.1 above, the UAE requires all financial institutions to identify the beneficial owners of a legal person customer by obtaining and verifying the identity of all individuals who, individually or jointly, have a controlling ownership interest in the legal person of 25% or more. Where no such individual meets this description, the LFI must identify and verify the identity of the individual holding the senior management position in the entity.
The AML-CFT Decision does not define “senior management position,” and LFIs should make a judgment, based on the specific facts and circumstances, as to the individual who meets this description. The senior management official should be a single individual with significant responsibility to control, manage, or direct a legal person customer. This may include the entity’s Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Chief Operating Officer, Managing Director, General Partner, or President.
LFIs should consider whether the individual’s background, experience, and expertise make it plausible that they would indeed hold a position of responsibility at a legal person of the customer’s size. Where a customer identifies a relatively young or inexperienced individual as its senior manager, that may be a sign that the individual does not in fact control the customer and instead takes orders from another individual who wishes to obscure his or her identity.
For legal arrangement customers, LFIs must verify the identity of the settlor and the trustee (or anyone holding equivalent positions for non-trust legal arrangements), the beneficiaries or class of beneficiaries, and any other individuals in control of the legal arrangement.
The beneficial owner of a legal person or arrangement must be an individual. Another legal person or arrangement cannot be the beneficial owner of a customer, no matter what percentage it owns. LFIs must continue tracing ownership all the way up the ownership chain until it discovers all individuals who own or control at least 25% of the LFI’s customer.
When the LFI has identified qualifying beneficial owners, it should perform CDD on each individual beneficial owner, in accordance with the requirements of Article 8.1(a) of AML-CFT Decision. Where the customer is a UAE legal person, LFIs may require the customer provide the beneficial ownership report it has submitted to its company registrar as per Cabinet Decision (58). This should not be a substitute, however, for independent identification of beneficial owners by the LFI.
LFIs are also required to understand the customer’s ownership and control structure. This means that LFIs must be aware of who owns the customer, even if they have not verified the identity of the individuals owning every company in the customer’s ownership chain. LFIs should have confidence that they fully understand who has the power to direct and control their customer’s actions.
4.3.2.2. Applying a Risk Based Approach
It is important to note that the legal requirements mentioned above (section 4.3.2.1) are baseline obligations rather than definitions of beneficial ownership. A beneficial owner, as defined in AML-CFT Decision, is any individual who owns or controls all or part of a legal person. This means that a legal person can have several beneficial owners, not all of whom are required to be identified under the law. LFIs should always identify and verify the identity of all individuals owning or controlling at least 25% of a legal person, but they should also make a risk-based decision as to whether to identify and verify the identity of additional beneficial owners. For legal person customers that require EDD, whether as a function of law or because they are higher risk, LFIs should always consider lowering the ownership threshold below 25%.
LFIs should be aware that even minority owners of a legal person customer can exercise control over the legal person through information arrangements, family relationships, and specific governance arrangements (e.g. preferred stock), among other methods. Customers whose minority owners include individuals that are subject to United Nations or UAE sanctions may also create serious risks for LFIs, even if the individual only owns a small share of the customer (see section 4.5 below). Thus, particularly in higher risk scenarios, LFIs should consider completing an ownership and control chart that includes at least the names of all beneficial owners of every legal customer, or all individuals owning at least 5% of the customer. Collecting the names of beneficial owners is distinct from identifying them and verifying their identity and does not require the LFI to collect identifying information. LFIs must still identify and verify the identity of all individuals owning at least 25% of legal person customers.
Beyond lowering the ownership threshold, EDD methods related to identification of ownership and control can include requiring the beneficial owners of customers to verify their ownership by presenting share certificates or contracts.
Example 1: Company A is a UAE-based company that leases office space. Company A applies to open an account with Bank Lion, a CBUAE-supervised LFI. Bank Lion verifies that Company A is 50% owned by Mr. Y and 40% owned by Ms. W. Bank Lion is aware that Company A has additional owners, but knows they own less than 10% of Company A.
Because Company A is a low-risk domestic firm, Bank Lion is not required to identify the additional owners of Company A.
Example 2: Company B is a Cayman Islands-based company with no business operations and a letterbox address on the premises of a known Cayman Islands TCSP. Company B applies to open an account with Bank Lion, a CBUAE-supervised LFI. Bank Lion verifies that Company B is 50% owned by Mr. Y, a citizen of Russia and 40% owned by Ms. W, a citizen of Malta.
Company B is likely a shell company, and its known beneficial owners are from high-risk jurisdictions. Therefore, Bank Lion decides to take the step of identifying and verifying the identity of the individuals who owns the remaining 10% of the company before accepting Company B as a customer. It discovers that the remaining 10% of shares are owned by Mr. Y’s father, a well-known Russian businessman. Because Mr. Y is only 22 and a recent university graduate, Bank Lion suspects that Mr. Y is a nominee and that his father may be the true controlling owner of Company B.
4.3.2.3. Legal Persons – Common Situations
In many cases, identifying the beneficial owners of a legal person customer will be a straightforward process. A customer may be directly owned by one or two individuals:
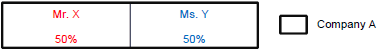
In such cases, an LFI is obliged to identify and to verify the identity of both individuals, Mr. X and Ms. Y.
Legal persons may have more complex ownership structures, however, in which other legal persons are involved in the ownership chain. In such cases, LFIs must continue up the chain until they identify an individual:
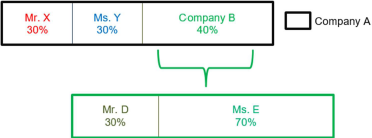
In this situation, the owners of Company A are as follows:
Owner Share Ownership Type Mr. X 30% Direct Ms. Y 30% Direct Ms. E 28% Indirect - Ms E owns 70% of Company B, which in turn owns 40% of Company A Mr. D 12% Indirect - Mr. D owns 30% of Company B, which in turn owns 40% of Company A Mr. X, Ms. Y, and Ms. E must all be identified under UAE law, as they own at least 25% of Company A. Mr. D owns 12%, so he is not required to be identified. But the LFI should make a risk-based decision as to whether to identify him.
Illicit actors may seek to use complex ownership structures to hide the fact that they own 25% or more of the customer. This is why it is important for LFIs to use a risk-based approach and to be confident that, at the end of the process, they fully understand who controls their customer.
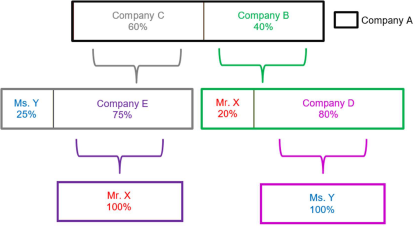
In this situation, although it at first appears that Ms. Y and Mr. X each own less than 25% of Company A, in fact between them they own 100% of the company. Their ownership interests can be calculated as follows:
Mr. X:
• 20% of Company B, which owns 40% of Company A: 20% of 40% is 8%; plus • 100% of Company E, which owns 75% of Company C, which owns 60% of Company A: 100% of 75% of 60% is 45%. • Mr. X owns 53% of Company A.
Ms. Y:
• 25% of Company C, which owns 60% of Company A: 25% of 60% is 15%; plus • 100% of Company D, which owns 80% of Company B, which owns 40% of Company A: 100% of 80% of 40% is 32%. • Ms. Y owns 47% of Company A.
Both Mr. X and Ms. Y must be identified under UAE law. In addition, LFIs should be aware that Mr. X and Ms. Y are likely associated parties and should question whether there is a legitimate economic purpose for the ownership structure of Company A.
4.3.2.4. Legal Arrangements - Common Situations
Legal arrangements may not present the layered ownership structures seen in legal persons. This does not mean, however, that identifying the beneficial owners of legal arrangements is always straightforward. In particular, the very different forms of legal arrangements that may be formed in different jurisdictions can make it difficult to identify the individuals who hold roles analogous to settlor, trustee, and beneficiary. LFIs should always identify the following individuals:
• The legal entities or individuals who have the power to control the property of the legal arrangements. These legal entities or individuals are analogous to trustees. If a legal entity (such as a financial institution) acts as trustee, LFIs must identify the beneficial owners of that legal entity. • The legal entities or individuals for whose present or future benefit the trustees are safeguarding the legal arrangement property. These legal entities or individuals are analogous to the beneficiaries. o Beneficiaries may be defined as a class which can change over time (e.g., “all the underage grandchildren of the settlor”). o LFIs should identify the class of beneficiaries, and all beneficiaries currently in existence, at the time of onboarding the customer. During periodic CDD refresh, they should ascertain whether additional identifiable individuals have joined or left the beneficiary class (e.g. a new child has been born, a beneficiary has come of legal age). o If a legal entity is the named beneficiary, LFIs must identify the beneficial owners of that legal entity. • The legal entities or individuals who assigned control of the legal arrangement property to the trustees (or individuals holding a similar position). This individual or legal entity is analogous to the settlor. A settlor may or may not retain underlying legal ownership of the legal arrangement property. If a legal entity acts as settlor, LFIs must identify the beneficial owners of that legal entity.
In addition, where trustees are financial institutions, lawyers or any other professional with secrecy rules in a foreign jurisdiction, it may be difficult to obtain the information LFIs need. LFIs should be aware that if they cannot obtain this information, they should not establish the business relationship or continue an existing relationship.
Legal arrangements may also be part of the ownership structures of other legal persons or arrangements. Because trusts do not have shares or equity, LFIs should treat all participants in a trust or similar legal arrangement as if they own 100% of the legal arrangement.
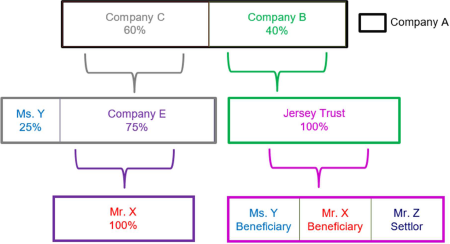
In the example above, Company A is 40% owned by Company B, which is in turn wholly owned by a trust established in the Isle of Jersey. Ms. Y and Mr. X are beneficiaries of the trust and also indirectly own shares of the Company A through Company C. Mr. X has to be identified and verified based solely on his indirect 45% ownership of Company A through Company E. Ms. Y and Mr. Z, must also be identified and verified because they are beneficial owners of a legal arrangement that owns 40% of Company A.